
It's a fear state in which you confront the danger of being assaulted or otherwise harmed so that you can defend yourself. It's an active self-preservation function when it's used as a trauma response, in which you move reactively toward conflict with anger and aggression. When functioning properly, the fight response enables for assertion and solid boundaries. However, while trauma is a major cause of internal upheaval, it may be taken to an unhealthy and wearing extent. Healthy stress responses aren't inherently negative they can help you stand up for yourself in the short term. If a problem is left unresolved, past trauma may turn into trapped, frozen energy that your body will respond to physiologically in the form of a trauma response.įight, flight, freeze, fawn: the four types of trauma response. They may not seem serious at the time, but the long-term effects of trauma can still have a significant influence on you physically, spiritually, and mentally when they are not emotionally processed and integrated-somatically, intellectually. Trauma, for example, might include a terrible breakup, a betrayal of trust, a work environment that is chronically abusive, or anything else that is mildly frightening over time.
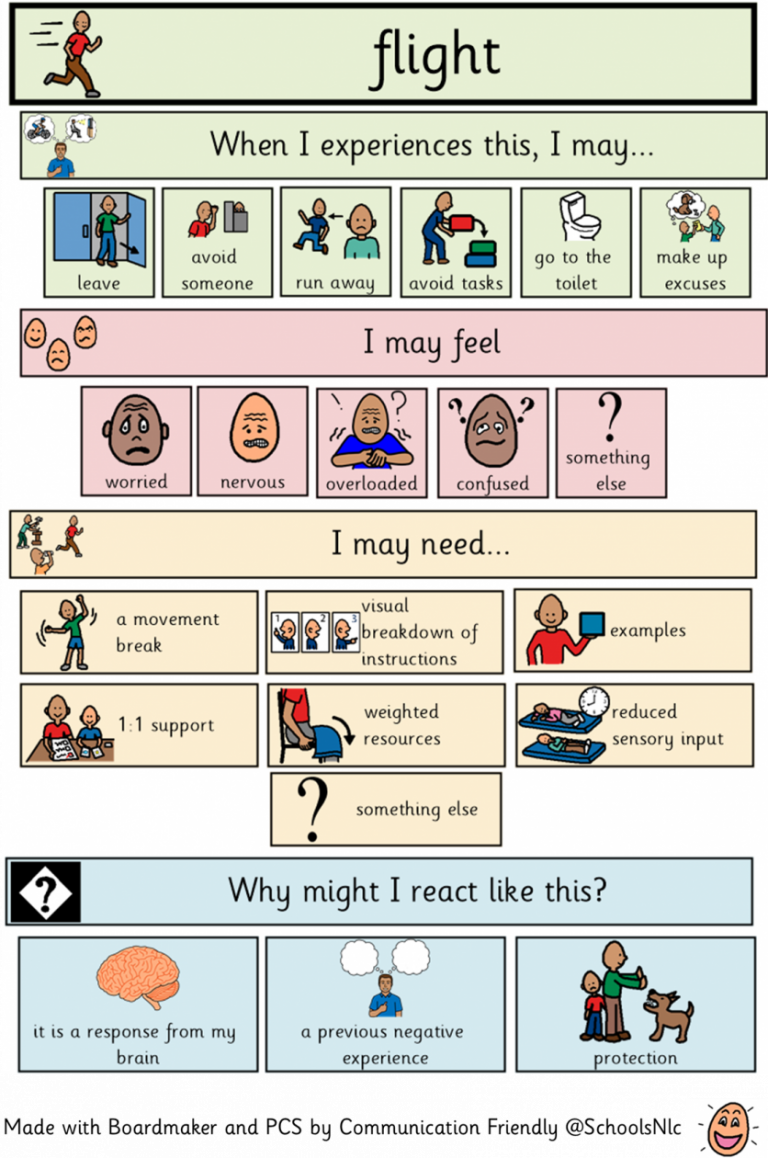

Because trauma is subjective and personal, minor "T" incidents may be just as traumatic as big "T" events. The fact is that trauma exists along a continuum of stress. These post-trauma responses, on the other hand, aren't limited to those who've experienced significant "Trauma" events (such as war, death, or disaster) frequently associated with profound trauma. The short-term protections become permanent as our body undergoes sympathetic nervous system dominance.
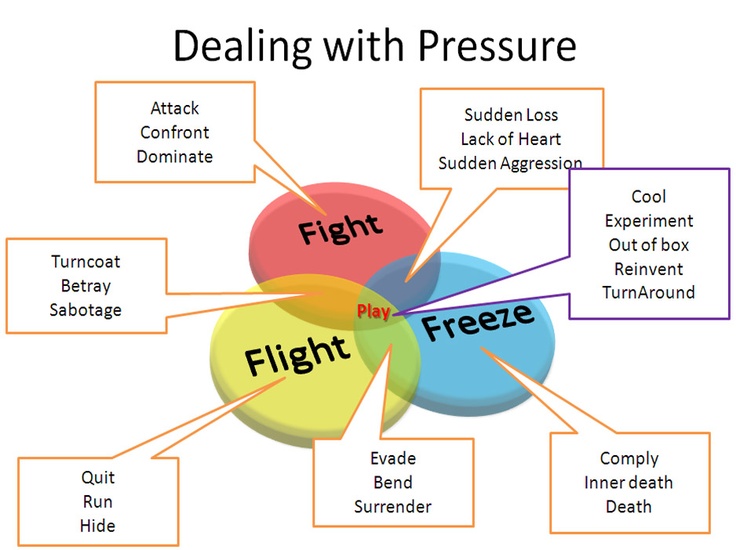
However, when our stress responses are continually activated, there isn't enough time to break down the chemicals, and our nervous system becomes overloaded and dysregulated-placing us firmly in the survival mode. Chemicals are introduced into our circulation via a short-term technique in order to rouse the body's defensive measures through the sympathetic nervous system. According to a research on the neurobiological consequences of psychological trauma, our bodies are designed to respond to perceived threats with a set of near-instantaneous, reflexive survival behaviors.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
